Handler&Pipeline
1. 概述
ChannelHandler用来处理Channel上的各种事件,分为入站、出站两种。所有ChannelHandler被连成一串,就是Pipeline。
- 入站处理器通常是
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter的子类,主要用来读取客户端数据,写回结果 - 出站处理器通常是
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter的子类,主要对写回结果进行加工
可以理解ChannelHandler就是数据处理的工序,各种工序按照顺序组合在一起就是流水线Pipeline, ByteBuf就是原材料,经过一道道出站工序最终变成产品,整个过程就是车间Channel中处理。
2. ChannelPipeline
ch.pipeline()会得到ChannelPipeline对象,里面包含了ChannelHandler列表,里面默认提供了Head和Tail两个ChannelHandler。
ChannelPipeline实现了拦截器设计模式,用于处理和拦截Channel的入站事件和出站操作。 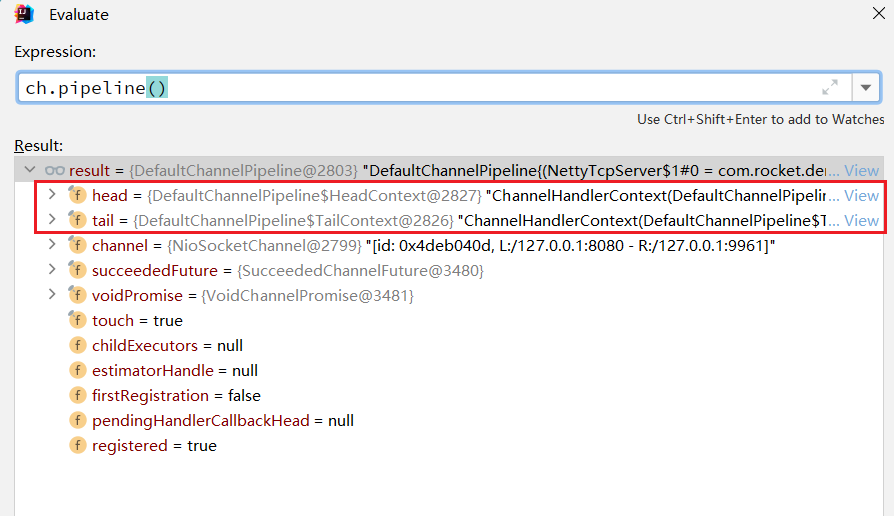
2.1 添加ChannelHandler处理器
使用addLast()方法在尾部添加处理器,addFirst()方法在头部添加处理器:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(new NioEventLoopGroup());
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast("readHandler1", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
logger.info("readHandler1收到的数据:{}", byteBuf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); // 将数据传递给下一个handler
}
});
ch.pipeline().addLast("writeHandler1", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
logger.info("writeHandler1");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
ch.pipeline().addLast("writeHandler2", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
logger.info("writeHandler2");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
}
});
bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)).sync();
}运行效果: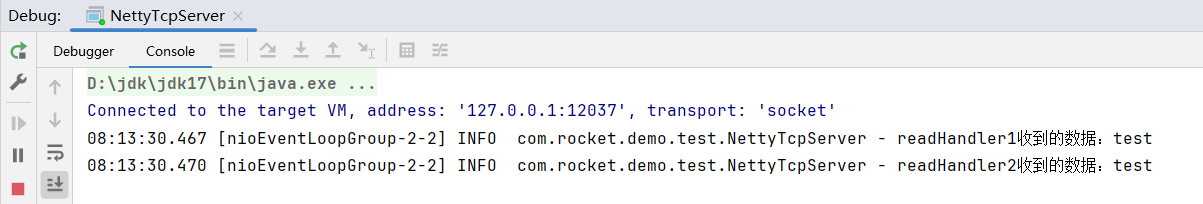 可以看到写操作的handler并没有触发,这是因为当前并没有数据真正的写出, 默认只会触发入站处理器。
可以看到写操作的handler并没有触发,这是因为当前并没有数据真正的写出, 默认只会触发入站处理器。
3. 入站处理器
主要使用的有ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter、SimpleChannelInboundHandler,区别在于前者支持可以把消息数据往后传递,SimpleChannelInboundHandler会把消息释放掉,导致后面的handler拿不到消息。
4. 出站处理器
主要使用的有ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter。
5. ChannelHandler执行顺序
入站处理器中,ctx.fireChannelRead(msg)是调用下一个入站处理器,也可以调用super.channelRead(ctx, msg);底层实际就是执行的ctx.fireChannelRead(msg)。 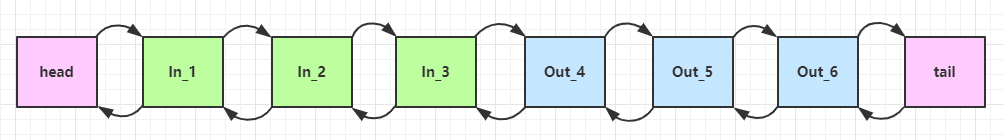 入站处理器中,调用
入站处理器中,调用ch.writeAndFlush(msg)会从尾部开始触发后续出站处理器的执行或者在出站处理器中调用ctx.writeAndFlush(msg)会触发上一个出站处理器
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(new NioEventLoopGroup());
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast("readHandler1", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
logger.info("readHandler1收到的数据:{}", byteBuf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); // 将数据传递给下一个handler
}
});
ch.pipeline().addLast("readHandler2", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
logger.info("readHandler2收到的数据:{}", byteBuf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
// ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); 因为后面是输出handler,如果不需要客户端数据可以不传
ch.writeAndFlush(ctx.alloc().buffer().writeBytes("hello world".getBytes()));
}
});
ch.pipeline().addLast("writeHandler1", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
logger.info("writeHandler1");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
ch.pipeline().addLast("writeHandler2", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
logger.info("writeHandler2");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
}
});
bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)).sync();
}运行效果: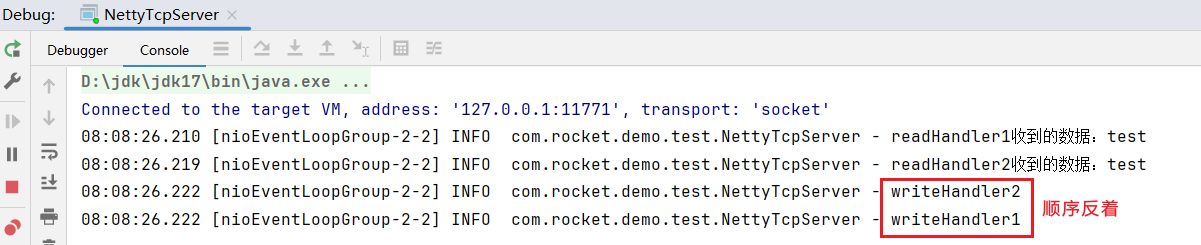
6. EmbeddedChannel
使用EmbeddedChannel可以帮助我们调试handler,而不用启动Netty服务器和客户端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter h1 = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
logger.info("1收到的数据:{}", msg);
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); // 将数据传递给下一个handler
}
};
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter h2 = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
logger.info("2收到的数据:{}", msg);
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); // 将数据传递给下一个handler
}
};
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter h3 = new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
logger.info("3收到的数据:{}", msg);
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
};
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter h4 = new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
logger.info("4收到的数据:{}", msg);
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
};
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(h1, h2, h3, h4);
// 模拟客户端发送数据
channel.writeInbound(ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer().writeBytes("123456789".getBytes()));
// 模拟服务端发送数据
channel.writeOutbound(ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer().writeBytes("hello".getBytes()));
}运行结果: 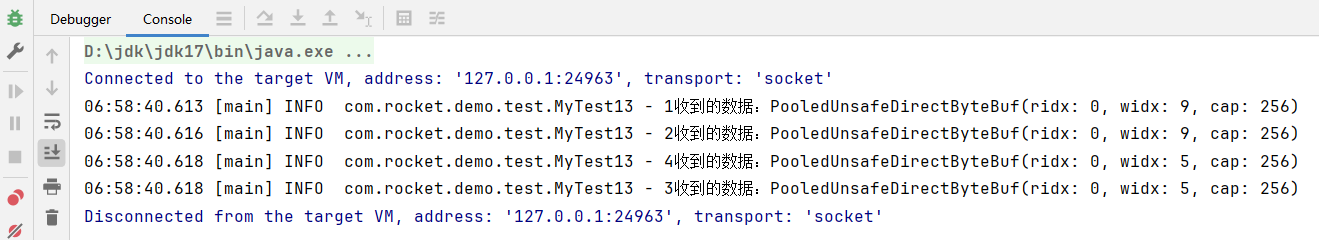
writeInbound()方法也就是入栈方法,表示服务端读消息;writeOutbound()方法为出栈方法,表示服务端写出消息。
7. 重复使用Handler
在ChannelInitializer中的initChannel()方法会每次请求都会执行,因此里面配置的handler每次请求都会被创建,造成Handler的利用率很低。
如果要重复使用相同的Handler就涉及到是否需要记录上一次请求状态(比如请求的数据内容),如果每次请求在Handler中处理没有关系(比如不关心半包粘包),就可以直接重用Handler。在Netty中使用@Sharable注解区分是否可以重用,很多Handler比如:ByteArrayEncoder、Base64Decoder、Base64Encoder、LoggingHandler都可以直接使用单例即可。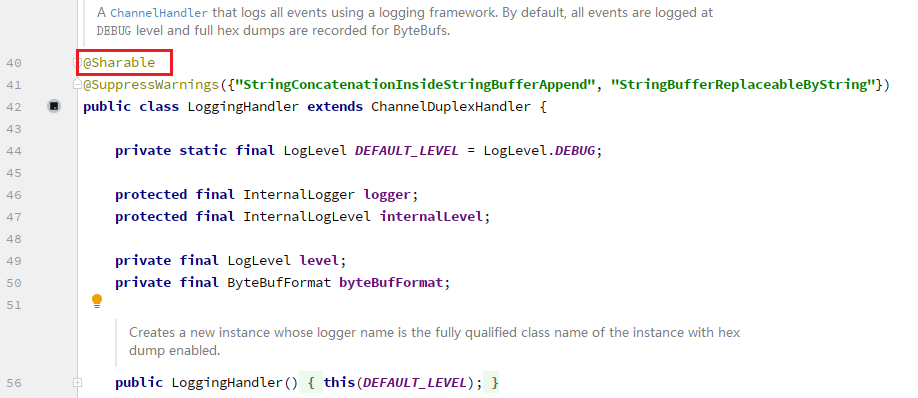 但要注意对于编解码器类,不能继承ByteToMessageCodec或CombinedChannelDuplexHandler父类,他们的构造方法对@Sharable都有限制。如果能确保编解码器不会保存状态,可以继承MessageToMessageCodec父类。
但要注意对于编解码器类,不能继承ByteToMessageCodec或CombinedChannelDuplexHandler父类,他们的构造方法对@Sharable都有限制。如果能确保编解码器不会保存状态,可以继承MessageToMessageCodec父类。
