密码加密机制
参考文档:Password Storage :: Spring Security
1. 密码存储演进
1.1 明文密码
最初,密码以明文形式存储在数据库中。但是恶意用户可能会通过SQL注入等手段获取到明文密码,或者程序员将数据库数据泄露的情况也可能发生。
1.2 Hash算法
Spring Security的PasswordEncoder接口用于对密码进行单向转换,从而将密码安全地存储。对密码单向转换需要用到哈希算法,例如MD5、SHA-256、SHA-512等,哈希算法是单向的,只能加密,不能解密。
因此,数据库中存储的是单向转换后的密码,Spring Security在进行用户身份验证时需要将用户输入的密码进行单向转换,然后与数据库的密码进行比较。
因此,如果发生数据泄露,只有密码的单向哈希会被暴露。由于哈希是单向的,并且在给定哈希的情况下只能通过暴力破解的方式猜测密码。
彩虹表
恶意用户创建称为彩虹表的查找表。彩虹表就是一个庞大的、针对各种可能的字母组合预先生成的哈希值集合,有了它可以快速破解各类密码。越是复杂的密码,需要的彩虹表就越大,主流的彩虹表都是100G以上,目前主要的算法有LM, NTLM, MD5, SHA1, MYSQLSHA1, HALFLMCHALL, NTLMCHALL, ORACLE-SYSTEM, MD5-HALF。
1.3 加盐密码
为了减轻彩虹表的效果,开发人员开始使用加盐密码。不再只使用密码作为哈希函数的输入,而是为每个用户的密码生成随机字节(称为盐)。盐和用户的密码将一起经过哈希函数运算,生成一个唯一的哈希。盐将以明文形式与用户的密码一起存储。然后,当用户尝试进行身份验证时,盐和用户输入的密码一起经过哈希函数运算,再与存储的密码进行比较。唯一的盐意味着彩虹表不再有效,因为对于每个盐和密码的组合,哈希都是不同的。
1.4 自适应单向函数
随着硬件的不断发展,加盐哈希也不再安全。原因是,计算机可以每秒执行数十亿次哈希计算(黑客不断的攻击消耗我们服务器资源,生成他们所需要的彩虹表)。这意味着我们可以轻松地破解每个密码。
现在,开发人员开始使用自适应单向函数来存储密码。使用自适应单向函数验证密码时,故意占用资源(故意使用大量的CPU、内存或其他资源)。自适应单向函数允许配置一个“工作因子”,随着硬件的改进而增加。我们建议将“工作因子”调整到系统中验证密码需要约一秒钟的时间。这种权衡是为了让攻击者难以破解密码。
自适应单向函数包括bcrypt、PBKDF2、scrypt和argon2。
2. PasswordEncoder
针对bcrypt、PBKDF2、scrypt和argon2算法,SpringSecurity提供了对应的PasswordEncoder类实现:
2.1 BCryptPasswordEncoder
使用广泛支持的bcrypt算法来对密码进行哈希。为了增加对密码破解的抵抗力,bcrypt故意设计得较慢。和其他自适应单向函数一样,应该调整其参数,使其在您的系统上验证一个密码大约需要1秒的时间。BCryptPasswordEncoder的默认实现使用强度10。建议您在自己的系统上调整和测试强度参数,以便验证密码时大约需要1秒的时间。
2.2 Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder
使用PBKDF2算法对密码进行哈希处理。为了防止密码破解,PBKDF2是一种故意缓慢的算法。与其他自适应单向函数一样,它应该在您的系统上调整为大约1秒来验证一个密码。当需要FIPS认证时,这种算法是一个很好的选择。
2.3 SCryptPasswordEncoder
使用scrypt算法对密码进行哈希处理。为了防止在自定义硬件上进行密码破解,scrypt是一种故意缓慢的算法,需要大量内存。与其他自适应单向函数一样,它应该在您的系统上调整为大约1秒来验证一个密码。
2.4 Argon2PasswordEncoder
使用Argon2算法对密码进行哈希处理。Argon2是密码哈希比赛的获胜者。为了防止在自定义硬件上进行密码破解,Argon2是一种故意缓慢的算法,需要大量内存。与其他自适应单向函数一样,它应该在您的系统上调整为大约1秒来验证一个密码。当前的Argon2PasswordEncoder实现需要使用BouncyCastle库。
3. BCryptPasswordEncoder源码
3.1 使用BCryptPasswordEncoder
@Test
public void testBCrypt() {
BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(10);
String result = encoder.encode("123456");
System.out.println(result);
//密码校验
Assert.isTrue(encoder.matches("123456", result), "密码不一致");
}可以指定加密耗时,在构造函数中传入strength参数即可:new BCryptPasswordEncoder(), 默认strength为10,官方称为工作因子,最小值是4,最大值是31,值越大运算速度越慢。另外每次执行会发现加密后的密码都不一样,可以看到源码中encode()方法有加盐处理:
@Override
public String encode(CharSequence rawPassword) {
if (rawPassword == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("rawPassword cannot be null");
}
String salt = getSalt();
return BCrypt.hashpw(rawPassword.toString(), salt);
}进入getSalt()方法:
// 可以看到加盐的组成有:版本号+工作因子+随机数
private String getSalt() {
if (this.random != null) {
return BCrypt.gensalt(this.version.getVersion(), this.strength, this.random);
}
return BCrypt.gensalt(this.version.getVersion(), this.strength);
}4. DelegatingPasswordEncoder
我们会发现表中存储的密码形式:{bcrypt}$2a$10$GRLdNijSQMUvl/au9ofL.eDwmoohzzS7.rmNSJZ.0FxO/BTk76klW
既然默认使用BCryptPasswordEncoder进行加密密码,为何加密结果长得不一样的呢?原因是SpringSecurity使用的是加密代理类DelegatingPasswordEncoder做实际加密处理的。  底层其实调用
底层其实调用PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder()方法,进入createDelegatingPasswordEncoder():
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static PasswordEncoder createDelegatingPasswordEncoder() {
String encodingId = "bcrypt";
Map<String, PasswordEncoder> encoders = new HashMap<>();
encoders.put(encodingId, new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("ldap", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.LdapShaPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD4", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.Md4PasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("MD5", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("MD5"));
encoders.put("noop", org.springframework.security.crypto.password.NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance());
encoders.put("pbkdf2", Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder.defaultsForSpringSecurity_v5_5());
encoders.put("pbkdf2@SpringSecurity_v5_8", Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder.defaultsForSpringSecurity_v5_8());
encoders.put("scrypt", SCryptPasswordEncoder.defaultsForSpringSecurity_v4_1());
encoders.put("scrypt@SpringSecurity_v5_8", SCryptPasswordEncoder.defaultsForSpringSecurity_v5_8());
encoders.put("SHA-1", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-1"));
encoders.put("SHA-256",
new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.MessageDigestPasswordEncoder("SHA-256"));
encoders.put("sha256", new org.springframework.security.crypto.password.StandardPasswordEncoder());
encoders.put("argon2", Argon2PasswordEncoder.defaultsForSpringSecurity_v5_2());
encoders.put("argon2@SpringSecurity_v5_8", Argon2PasswordEncoder.defaultsForSpringSecurity_v5_8());
return new DelegatingPasswordEncoder(encodingId, encoders);
}其中encodingId默认就是bcrypt,对应BCryptPasswordEncoder对象。也就说DelegatingPasswordEncoder内部默认加解密使用的就是BCryptPasswordEncoder对象。
4.1 加密
在DelegatingPasswordEncoder的encode()方法中, 可以看到加密后的密码就是由idPrefix+idForEncode+idSuffix+BCryptPasswordEncoder加密的密码: 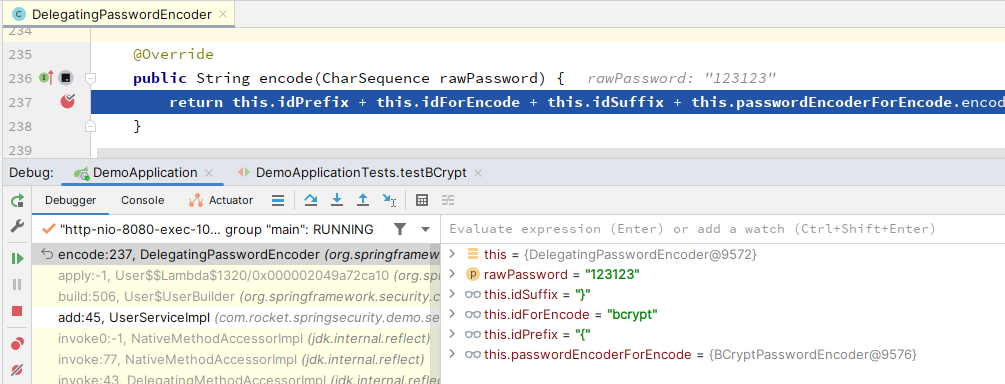 其中idForEncode就是加密算法。
其中idForEncode就是加密算法。
4.2 密码匹配
@Override
public boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String prefixEncodedPassword) {
if (rawPassword == null && prefixEncodedPassword == null) {
return true;
}
// 从密码中得到加密方式
String id = extractId(prefixEncodedPassword);
// 得到对应的算法的加解密类
PasswordEncoder delegate = this.idToPasswordEncoder.get(id);
if (delegate == null) {
return this.defaultPasswordEncoderForMatches.matches(rawPassword, prefixEncodedPassword);
}
// 脱掉密文中的idPrefix+idForEncode+idSuffix
String encodedPassword = extractEncodedPassword(prefixEncodedPassword);
return delegate.matches(rawPassword, encodedPassword);
}这样设计保存的密码,目的是为了方便随时做密码策略的升级,兼容数据库中的老版本密码策略生成的密码
